Global LEO Satellite Market Overview
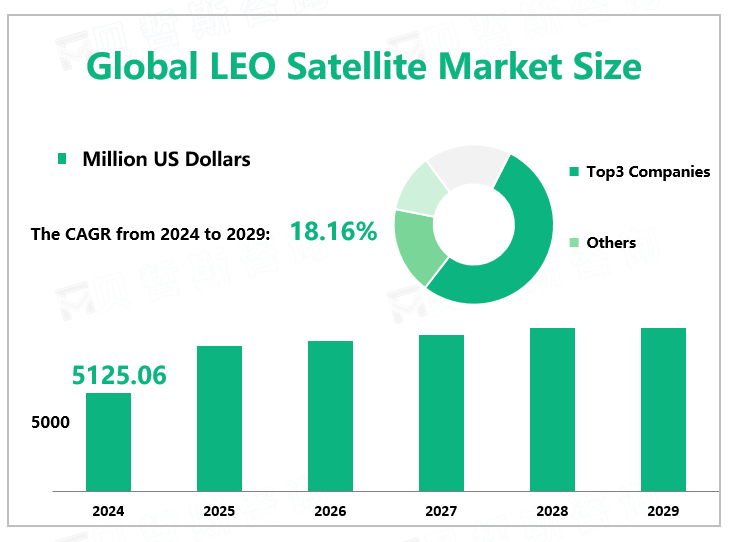
According to Global Market Monitor, the global LEO satellite market size will reach $5125.06 million in 2024 with a CAGR of 18.16% from 2024 to 2029.
Low Earth orbit refers to an orbit around the Earth 2,000 kilometers above the surface and is commonly used in communications, military surveillance, spy, and other imaging applications.
Increase in Downstream Applications
As downstream applications expand, so does the demand for LEO-based services. GEO satellites have many applications, including weather forecasts, satellite radio, and television. With the rapid development of the Internet, customers' demand for low-latency, high-speed broadband network services is increasing. Low-orbit satellite communications can achieve wide-area coverage compared to terrestrial communication networks, making it impossible for remote areas, aircraft, ships, and other terrestrial networks. These market drivers are currently stimulating the development of Low-Earth orbit satellites.
The growing demand for high-speed Internet connectivity, especially in rural and underserved areas, is driving the demand for broadband services for Low-Earth orbit satellites. With low latency and high data rates, LEO satellites are the best choice for real-time data transfer applications such as video streaming, gaming, and remote working. There is a growing demand for remote sensing applications based on low Earth orbit satellites in many sectors, including forestry, agriculture, and energy. LEO satellites provide high-resolution images and real-time data on environmental and climatic conditions, enabling more effective decision-making.
Low-Earth Orbit Satellites Cost Less than Large Satellites.
Compared to traditional satellites, small satellites typically have shorter development cycles and smaller development teams, so the cost of satellite development and launch is lower. With the maturity of the satellite industry chain, the costs of manufacturing, launching, and operating are greatly reduced. Some satellite manufacturers have introduced technologies and production lines such as three-dimensional printing to achieve mass production of small satellites. This has promoted the expansion of the low-orbit satellite market.
Low Earth Orbital Crowding and "Space Garbage" Issues
As the frequency of satellite launches increases, the problem of space debris becomes more and more serious. Space around the earth has gradually become a large garbage dump, and the intensity of garbage has become a hot topic. Any new spacecraft heading for orbit must operate at a low enough altitude to re-enter the atmosphere when the mission is completed or to include a forced orbital mechanism to operate when necessary. The issue of space debris may hinder the future development of Low-Earth orbit satellites.
|
Iridium NEXT |
Proposed by MOTOROLA Inc. to provide mobile communications services to business users around the world. |
|
Starlink |
With the largest scale and number of launches of low-orbit constellations worldwide presently, proposed by the US SpaceX company. |
|
OneWeb |
OneWeb's low-orbit satellite constellation program. |
|
Kuiper |
Supported by Amazon, it has unique advantages in terms of capital and later application landing. |
|
Swan Goose |
China Aerospace Science and Technology |
|
Hong Yun |
China Aerospace Science and Industry |
We provide more professional and intelligent market reports to complement your business decisions.