Global Rare Earth Elements Market Overview
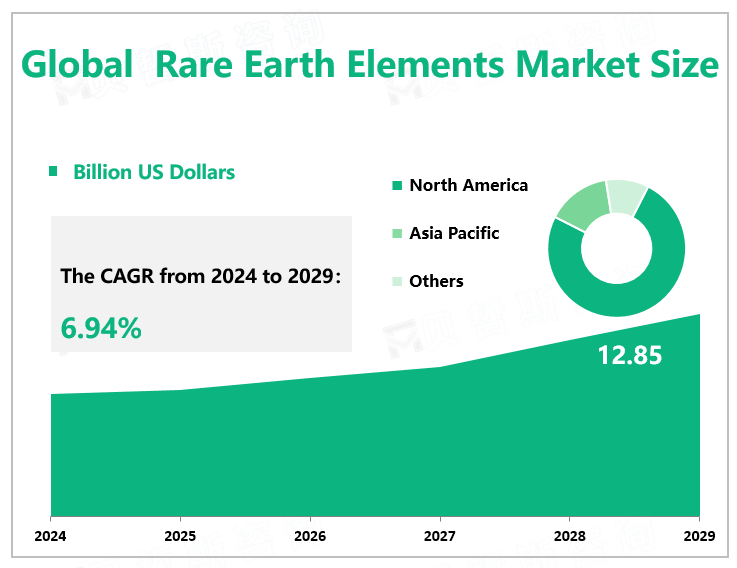
According to Global Market Monitor, the global rare earth elements market size is expected to grow to $12.85 billion by 2029 with a CAGR of 6.94% from 2024 to 2029. Rare earth elements are a set of seventeen chemical elements in the periodic table, specifically the fifteen lanthanides plus scandium and yttrium.
China is the Largest Country in Rare Earth
The Asia-Pacific region dominates the global market share. With increasing investment in the healthcare sector and increasing demand and production of ceramics, consumption of rare earth elements in the region is expected to increase significantly. According to the United States Geological Survey (USGS), as of the end of 2022, the total global rare earth reserves are about 130 million tons, and China's rare earth reserves are 44 million tons, accounting for 33.8% of the total global reserves. As the world's largest rare earth reserve and the largest producer, China's rare earth industry has continued to integrate in recent years.
India has the world's fifth-largest reserves of rare earth elements, about twice as much as Australia. Japan is looking to increase its reserves of rare earth minerals. In addition, the country is expected to help domestic companies acquire stakes in overseas mines and process raw materials into valuable minerals needed for next-generation cars, communications equipment, and other cutting-edge technologies. According to the United Nations Commodity Trade Statistics database, Japan has cut its rare earth supply from China from more than 90 percent of its imports to 58 percent in a decade. It aims to reduce that to less than 50% by 2025.
Application Fields
Due to the variety of rare earth elements and their wide application, the continuous development of these downstream applications is the main driving force of the market.
The permanent magnet industry is the largest end-user industry for rare earth elements. Lanthanum and cerium are used to make catalytic converters. These help convert contaminants in the engine's exhaust system into non-toxic compounds. A rechargeable battery made of neodymium, lanthanum, cerium, and praseodymium (combined with manganese, nickel, cobalt, and/or aluminum) is used in a car battery of a hybrid electric vehicle, an electronic device, and a power tool. Lanthanum and cerium are used in the manufacture of catalytic converters to convert contaminants in the engine exhaust system to non-toxic compounds. Electric and hybrid vehicles can contain many dollars of rare earth compounds, which is twice that of standard gasoline vehicles. The manufacture of batteries involves the use of rare earth compounds. Rare earth elements are also used in regenerative braking systems and electric traction motors. These motors consist of powerful magnets made of neodymium and dysprosium. Europium, terbium, and yttrium are rare earth elements that are widely used in the electronics industry to make LCD and color TVs. Cerium reduces the transmission of ultraviolet light, while lanthanum increases the glass reflectance index of digital camera lenses. Dysprosium, yttrium, neodymium, praseodymium, and terbium have the largest exposure to rechargeable batteries, phosphors, permanent magnets, and polishes. These market segments are also the fastest-growing segment of rare earth elements. As a result, a wide range of end-user applications have led to an increase in the use of rare earth elements worldwide.
|
By Type |
Cerium |
|
Dysprosium |
|
|
Erbium |
|
|
Europium |
|
|
Gadolinium |
|
|
Holmium |
|
|
Lanthanum |
|
|
Lutetium |
|
|
Neodymium |
|
|
Praseodymium |
|
|
The cerium segment contributes the largest market share. |
|
|
By Application |
Magnets |
|
Catalysts |
|
|
Metallurgy |
|
|
Polishing |
|
|
Glass |
|
|
Phosphors |
|
|
Ceramics |
|
|
The magnets segment occupies the biggest share. |
We provide more professional and intelligent market reports to complement your business decisions.