Global Fuel Cell for CHP Applications Market Overview
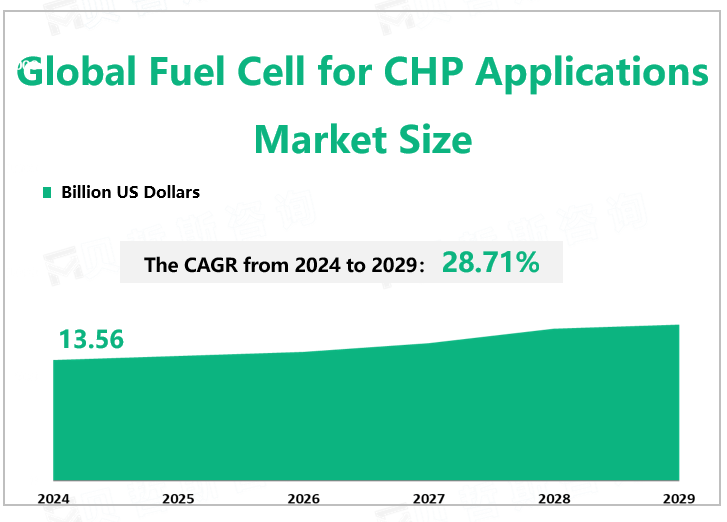
According to Global Market Monitor, the global fuel cell for CHP applications market size will reach $13.56 billion in 2024 with a CAGR of 28.71% from 2024 to 2029.
Fuel cells use electrochemical processes to convert chemical energy in the fuel into electrical energy. The CHP system involves the simultaneous generation of electricity and available heat from a power plant or heat engine in a single high-efficiency process. It captures the energy generated during power generation and uses it for commercial and residential heat production.
Market Dynamics
The hydrogen supply chain is very much in development. Reductions in fuel cell cost, volume, mass, and hydrogen storage cost have greatly contributed to enabling the initial Fuel Cell for CHP Applications market.Trigeneration has the greatest benefit when it comes to building or requiring permanent buildings that require electricity, heating, and cooling. Redundant power, lower power usage costs, and the ability to sell power back to the local grid in mission-critical applications are several major advantages. Increased energy use and this increased efficiency can also provide significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions.
The main market driver for fuel cells for cogeneration applications is the growing demand for clean energy aimed at reducing carbon emissions and their harmful effects on the environment. Other factors expected to drive the market growth are its operating characteristics such as higher efficiency and longer service life.
The major market constraint for the market is the high price of catalysts, which plays an important role in defining the operational efficiency of fuel cells. Another factor that may hinder the growth of the market is the lack of required fuel cell infrastructure in many countries.
Based on type, PEMFCs are expected to dominate the market due to their high energy retention capacity compared to other available comparable batteries. A proton exchange membrane fuel cell is a fuel cell that uses the proton exchange between permeable gas and water to generate electricity. Compared to conventional fuel cells, the operation is more efficient, however, due to its non-metallic nature, it operates at a lower temperature, and the main advantage of the technology is that it can be manufactured using low-cost materials such as ceramics.
Based on application, the non-residential sector accounts for the largest share of fuel cell use. Due to the growing demand for data centers and corporate offices, commercial and industrial buildings are increasingly in demand. With the increasing government support for installing fuel cells in homes as an alternative power supply source, the residential sector will also be significantly faster.
The Asia Pacific dominates the market share. Japan is the main market, followed by countries such as China, India, and Malaysia. This increase can be attributed to the high demand for cogeneration systems in Japan and other countries. North America and Europe follow the Asia Pacific market, with increasing fuel cell production in countries such as Italy, Germany, and the United States and the focus on renewable energy will drive growth in these regions in the coming years.
|
By Type |
PEMFC |
|
MCFC |
|
|
SOFC |
|
|
PAFC |
|
|
The PEMFC segment contributes the largest market share. |
|
|
By Application |
Residential |
|
Non-residential |
|
|
The non-residential segment occupies the biggest share. |
We provide more professional and intelligent market reports to complement your business decisions.