Global Underwater Robotics Market Overview
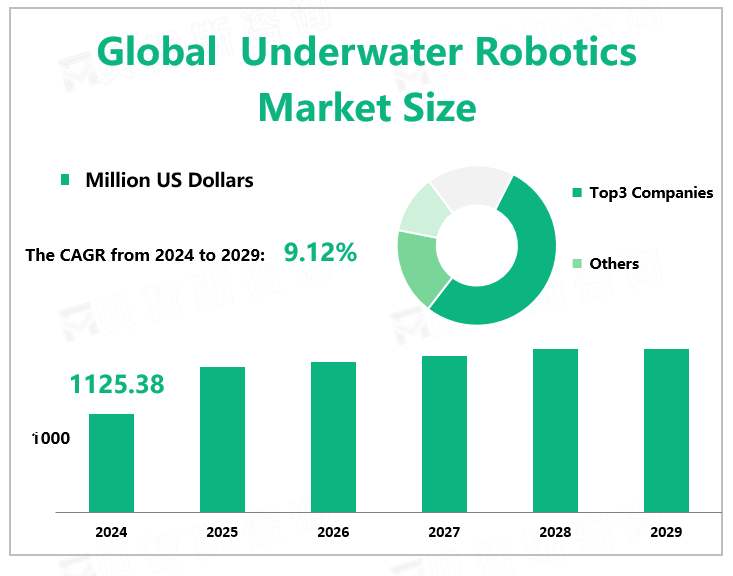
According to Global Market Monitor, the global underwater robotics market size will reach $1125.38 million in 2024 with a CAGR of 9.12% from 2024 to 2029.
An underwater Robot is a robot that can operate underwater without a human occupant. The underwater robot is used to monitor the operations undersea across the oil fields, discover new species of aquatic animals, and explore sunken ships, as it can drive, drift, or glide through oceans without the need for any human operator’s control. Furthermore, it is equipped with a video camera and the lights that are important to get the vision under the sea for research and detection.
Market Drivers
Scientists and researchers need more detailed and accurate data as global warming accelerates the exploration of unknown ocean areas. Underwater Robotics with advancements in technology and the advent of sophisticated measurement tools can satisfy these requirements.
High underwater performance drives the demand for Underwater Robotics. In the beginning, Underwater Robotics was mainly used for scientific explosions. Nowadays, diverse industries regard these as essential tools with complex functions, such as military and defense, oil and gas, and so on. It is generally equipped with a video camera and lights. There is additional equipment which is added to expand the underwater robots’ capabilities such as sonars, sound velocity, magnetometers, special cameras, temperature, a manipulator or cutting/shearing tools, water temperature, water samplers, and instruments that measure the water clarity, and the water density. These robots include functions such as equipment repair, searching and recovering, inspection, scientific analysis, cable-laying, surveying searching, and trenching.
Market News
Researchers at the University of California, Los Angeles, have developed a new technology that gives underwater robots a "sense of touch" to reduce the damage to Marine life when grabbing Marine debris. At the beginning of 2024, researchers published a paper in the journal Science Advances in the United States, and they used the magneto elastic effect to develop a soft, waterproof "artificial skin", that can convert tactile stimulation into magnetic field changes and then convert into electrical signals for artificial intelligence systems to interpret so that underwater robots can have a "sense of touch". The magnetoelastic effect refers to the phenomenon that the magnetic properties of magnetic materials change due to stress or strain. The researchers connected the "artificial skin" to the robot arm and let the robot arm randomly grab sea creatures such as sea snails, scallops, starfish, and Marine litter samples such as bottle caps, paper cups, and plastic bottles, and found that the "artificial skin" could help the robot arm identify these objects with a classification accuracy of 95%. The researchers said that this new technology can help robots recycle Marine garbage while reducing the damage to Marine life, and in deep-sea biological sampling, seabed mining and other fields also have application potential, to contribute to the sustainable development of Marine resources.
|
Market Drivers |
High Performance of Underwater Robotics |
|
More strict research requirements |
|
|
Perpetual underwater robotics |
|
|
No barriers to underwater communications |
|
|
Accurate positioning and navigation in depth zone |
|
|
Market Limitations |
High initial capital investment and R&D cost |
For more industry information, please refer to our latest released "2023 Global Underwater Robotics Market Analysis Report, Key Competitors, Market Effect Factors, Growth, And Forecast".
We provide more professional and intelligent market reports to complement your business decisions.